SERVIR's new web service streamlines use of key precipitation data
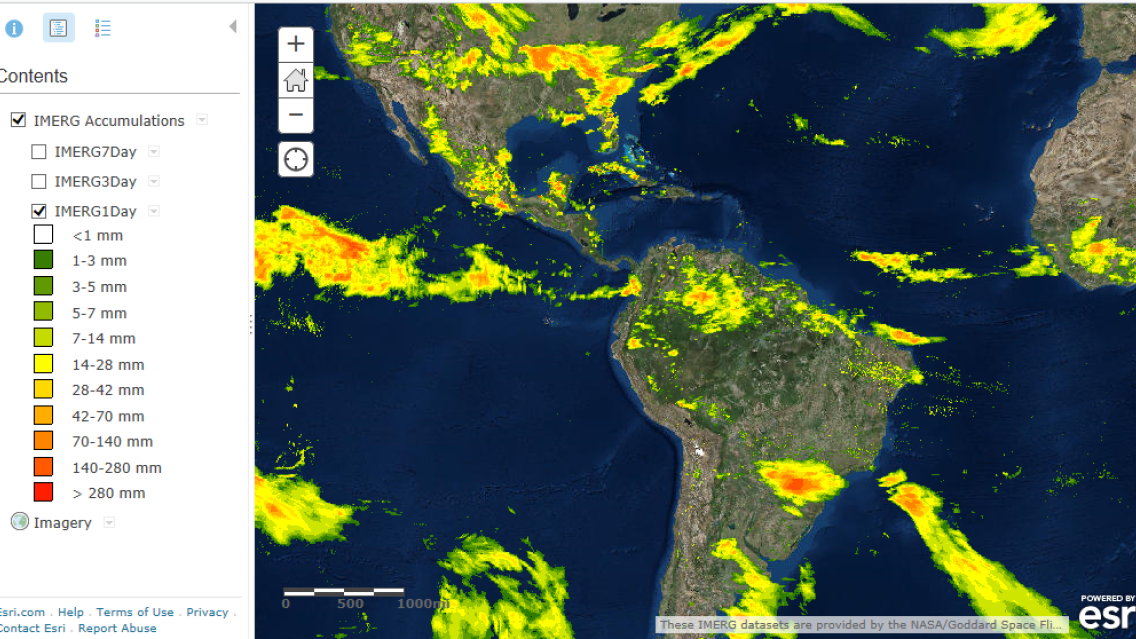
In 2014, NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) launched a new satellite that can see through storms and track rain and snow around the globe better than any previous observatory. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission offers the most accurate and comprehensive collection of precipitation data ever assembled. SERVIR has created an online web mapping service that makes it easier for national weather agencies, risk management agencies, researchers, and others to visualize and use this unprecedented information.
| GPM/IMERG 30 Minute intensity (time-series) |
Flying 253 miles above Earth in an orbit inclined 65-degrees to the equator, GPM can monitor precipitation all the way from the Arctic to the Antarctic circles. Working with a network of other satellites--some already in orbit and some planned for the future--GPM provides a near global picture of rain and snow at roughly 10-kilometer resolution all over the planet every 30 minutes. These detailed datasets about rain and snow systems are key to improving weather and climate forecasts. GPM’s instruments also enable a three-dimensional look at storms, which offers critical clues about how a storm is intensifying and where it might be moving. Providing all of this information, GPM helps researchers understand and predict extreme events like floods and droughts.
The precipitation data collected every 30 minutes from the GPM constellation is combined into a product called IMERG*. SERVIR’s map services extract this processed data from the publicly available data archive at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and make it available via a web mapping service. The service datasets, which include a 30-minute rainfall time-series over the past 90 days, as well as the latest 1-day, 3-day, and 7-day accumulation totals, can be visualized in any standard GIS client viewer that supports web map service data.
The map service endpoints are available at the following URLs:
- 30 Minute Intensity (time-series): https://gis1.servirglobal.net/arcgis/rest/services/Global/IMERG_30Min/MapServer
- 1, 3, and 7 Day Accumulations: https://gis1.servirglobal.net/arcgis/rest/services/Global/IMERG_Accumulations/MapServer
Notes:
GPM takes the place of and improves upon the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), which provided rainfall estimates from satellites for 17 years.
| GPM/IMERG 7-Day accumulation |
*IMERG (Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM data) is a unified algorithm that provides a merged multi-satellite precipitation product developed at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. The GPM team and the Precipitation Processing System (PPS) develop and compute IMERG. The products are archived and distributed by the Goddard Earth Science Distributive Active Archive Center (GES DAAC).
Data is downlinked through NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System to NASA's Precipitation Processing Center in Greenbelt, Md., where it is processed and distributed over the Internet.
For more information about GPM, see http://pmm.nasa.gov/gpm, http://pmm.nasa.gov/image-gallery/gpm-constellation, http://pmm.nasa.gov/education/videos/gpms-first-global-rainfall-and-snowfall-map, and http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/details.cgi?aid=11877.
For more information about IMERG, see http://pmm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/gpm.

